ROBOTIC PROCESS
AUTOMATION (RPA) FAQ
RPA continues to be one of the hot topics of the moment, but with the technology growing, more and more concepts and terms have emerged, making it a little confusing for the RPA newcomers. In order to clear things up here is a comprehensive compilation of all the key elements of RPA, what RPA is, how it works and when to apply it.
WHAT IS ROBOTIC
PROCESS AUTOMATION?
According to Gartner, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a productivity tool that allows a user to configure one or more scripts (which some vendors refer to as “bots”) to activate specific keystrokes in an automated fashion. The result is that the bots can be used to mimic or emulate selected tasks (transaction steps) within an overall business or IT process. These may include manipulating data, passing data to and from different applications, triggering responses, or executing transactions. RPA uses a combination of user interface interaction and descriptor technologies. The scripts can overlay on one or more software applications.
HOW IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION DIFFERENT FROM OTHER ENTERPRISE AUTOMATION TOOLS?
RPA is a transparent technology that works on UI layer which means that doesn’t require a complex integration with the current infrastructure ecosystem. Generally we can find different approaches of automations in enterprises and they are stricted to the scope that it was defined and built exclusively for the needs that try to solve. RPA goes far beyond that providing a flexible framework to develop automation which could include any system, application, web app, tool that works on a personal computer.
ROBOTIC PROCESS
AUTOMATION (RPA) FAQ
RPA continues to be one of the hot topics of the moment, but with the technology growing, more and more concepts and terms have emerged, making it a little confusing for the RPA newcomers. In order to clear things up here is a comprehensive compilation of all the key elements of RPA, what RPA is, how it works and when to apply it.
WHAT IS
ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
According to Gartner, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a productivity tool that allows a user to configure one or more scripts (which some vendors refer to as “bots”) to activate specific keystrokes in an automated fashion. The result is that the bots can be used to mimic or emulate selected tasks (transaction steps) within an overall business or IT process. These may include manipulating data, passing data to and from different applications, triggering responses, or executing transactions. RPA uses a combination of user interface interaction and descriptor technologies. The scripts can overlay on one or more software applications
HOW IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION DIFFERENT FROM OTHER ENTERPRISE AUTOMATION TOOLS?
RPA is a transparent technology that works on UI layer which means that doesn’t require a complex integration with the current infrastructure ecosystem. Generally we can find different approaches of automations in enterprises and they are stricted to the scope that it was defined and built exclusively for the needs that try to solve. RPA goes far beyond that providing a flexible framework to develop automation which could include any system, application, web app, tool that works on a personal computer.
HOW DOES THE ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION WORK?

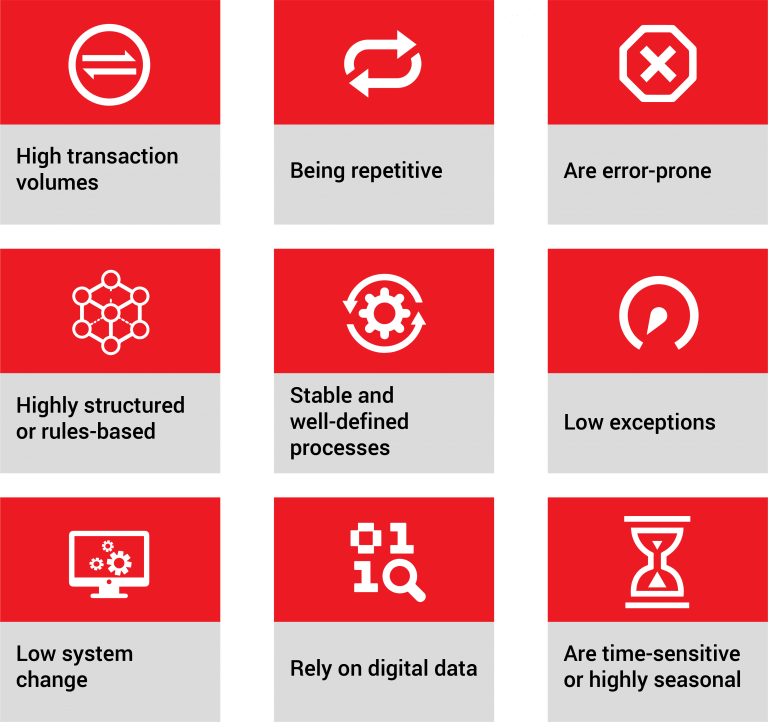
WHAT PROCESSES ARE RELEVANT TO ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
For RPA, the best processes are the ones that are repetitive, can be performed independently and cognitive in nature. Common selection attributes in order to make it suitable for RPA are:
WHAT ARE THE BUSINESS BENEFITS OF ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
There’s multiple benefits that RPA can bring, depending on the industry or process it is applied to. In general, companies implementing RPA can expect the following benefits from integrating RPA are:

WHAT SERVICES DOES A MSP ACTUALLY PROVIDE?
IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION DIFFERENT FROM ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)?
RPA is a software that uses a specific set of rules and an algorithm to automate a specific task and. AI is a cognitive solution that emulates human intelligence and is focused more on doing a human-level task. These two techs have the capability to take automation to the next level if both are combined.
IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION DIFFERENT FROM MACHINE LEARNING (ML)?
The difference between RPA and ML is that the former is rule-driven, while the latter is data-driven. Machine learning is both a part and a precursor of AI, as it already incorporates prescriptive analytics and can be used to run decision-making engines.
RPA is a software robot that mimics human actions, whereas AI and ML is the simulation of human intelligence by machines. Many people often asked about the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
WHAT ARE THE BEST ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION TOOLS?
The top 3 RPA tools in the market based on Gartner’s Magic Quadrant:
- Uipath
- Automation Anywhere
- Blue Prism
WHAT PROCESSES CAN ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION AUTOMATE?
Use cases for RPA have expanded into many functional areas. As mentioned by Gartner, here are some of the common activities where RPA it’s being applied:
- Accessing web/other enterprise applications
- Collecting statistics data from various applications
- Connecting to system APIs
- Copying and pasting
- Extracting structured data from documents
- Filling in forms
- Following if/then decisions/rules
- Making calculations
- Moving files and folders
- Opening Email and attachments
- Reading and writing to databases
- Scraping data from the web
WHAT ARE THE PROS AND CONS OF RPA?
RPA is a great option for many businesses, because of some of these key pros:
- Flexibility: RPA can be programmed to complete almost any repetitive task.
- Ease of implementation (for experts): RPA can be set up easily, simply by setting up a macro by recording your actions.
- Ease of Integration: RPA bots do not need to be integrated with most software..
As is the case with any technology, RPA has a few drawbacks:
- Only manage digital formats. Robots can’t read printed formats unless working with an OCR software.
- RPA is not a cognitive computing solution. RPA can’t learn from experience and therefore has a ‘shelf life’.
- RPA is not a fixer. applying RPA to inefficient processes will not fix them.
WHAT ARE BOTS IN ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION? IS CHATBOT AN RPA?
RPA stands for “ Robot Process Automation” however there is no robot as we might know as a physical robot, in fact a bot is a software trained to perform some action.
RPA is not a chatbot and it is more related to AI technology, however a chatbot could be a part of an RPA solution.
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A VIRTUAL ASSISTANT AND A CHATBOT?
Virtual assistant is a software that performs actions on behalf of a human, imitating his actions on a desktop computer. A chatbot is program used as a communication channel that is able to emulate communication human skills.
HOW IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION DIFFERENT FROM MACROS?
Macros are useful to automate simple and repetitive task performed on MS Excel, it has a macro recorder but Visual Basic knowledge is needed.
WHAT’S THE TESTING AUTOMATION VS PROCESS AUTOMATION?
Testing Automation as we know, it is mostly and mainly used for Web Applications and Mobile Application and it is the action to automate repetitive tasks for test an application. We can achieve the same with RPA and much more of that because we can perform many more actions, interact with Windows application, MS Office, systems application, etc.
WHAT’S HYPERAUTOMATION?
Named by Gartner as its #1 strategic technology trend for 2020, hyperautomation refers to the combination of multiple machine learning, packaged software and automation tools to deliver work. The propensity to use particular types of automation will be highly dependent on the organization’s existing IT architecture and business practices. Hyperautomation refers not only to the breadth of the pallet of tools, but also to all the steps of automation itself (discover, analyze, design, automate, measure, monitor, reassess).
Hyperautomation builds on the momentum behind RPA, led by the democratization of automation and IT and accelerated by the liberation of mundane and repetitive tasks for workers across every industry. In many ways, hyperautomation is redefining work.
WHAT’S THE BEST WAY TO START WITH ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
Heads of business departments should follow the next steps to develop an RPA implementation strategy that ensures its success and future scalability.
- Assess your company for automation opportunities
- Build your RPA business case
- Determine the optimal operating model
- Identify your automation partner(s)
- Plan the automation roadmap and RPA Governance plan
WHAT’S THE CHALLENGES FOR A ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION PROCESS?
There’s multiple challenges that can arise when trying to implement RPA in your company, here’s three of the major and most common ones:
- Employee resistance and onboarding
Any technology implementation comes with changes that can result in stress for employees, especially the ones that have been there for a while. In the case of RPA there’s also the belief that bringing in automation, equals to layoffs, creating some adoption resistance.
- Choosing the right processes
It is critical to determine which processes are suitable for RPA so that automation runs smoothly. This requires a thorough analysis and shouldn’t be rushed, as this might lead to failure to meet the expectations.
- Setting realistic expectations
RPA is often seen as the solution for all operational processes. Companies need to recognize the limits of what RPA can do and understand that RPA will not fix broken processes.
WHICH INDUSTRIES ARE ADOPTING RPA THE MOST?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been adopted in top industries during the last few years. Here’s the top six industries that are adopting RPA to change the way they do business.
- Utilities
- Banking
- Insurance
- Healthcare
- Telecommunications
- Manufacturing
