Introduction
When talking about databases, Oracle is one of the most trusted organizations in the world. Many of the capabilities, areas, performance, security, applications and management that Oracle is known for are powered thanks to many different already-released Oracle database versions.
As a result, Oracle’s reputation as a modern cloud provider continues to grow as the company continues to make significant advances in its database infrastructure. In fact, according to Gartner, Oracle continues to be a leader in DBMS technologies, and at the end of 2019, Oracle was the leader in DBMS revenue ($15.15 billion) and market share (27.5%).
Oracle’s portfolio spans multiple markets, among which, we can find Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) as one of its most successful flagship products. For years, Oracle EBS clients have leveraged the applications to support mission-critical tasks and continue to do so as Oracle has pledged its continued support and investment as part of their Continuous Innovation model under the Applications Unlimited program.
Database Compatibility and Interoperability
As part of the Oracle EBS roadmap, it’s worth mentioning that Continuous Innovation is available for release 12.2 of Oracle EBS. As such, EBS instances below this release will lose Premier Support by the end of December 2021, which is why it’s essential that you take immediate action to upgrade your EBS system as soon as possible.
When thinking about an upgrade to R12.2, the database is one of the most critical aspects to consider. There are two types of Oracle Database releases: long-term release and innovation release.
The long-term releases benefit from infrequent upgrades to the latest releases. This type of release offers the highest level of stability and the most extended amount of error correction support. Typically, these releases have five years of Premier Support with three years of Extended Support afterward. Typically, clients have approximately four years between having to upgrade from one long-term release to another.
The innovation releases deliver several enhancements and new capabilities that will also be packed inside the next long-term release. Innovation releases are built to help customers use cutting-edge technologies to quickly develop or deploy new apps or improve existing applications. Typically, innovation releases include two years of Premier Support with no option for Extended Support.
Oracle provides several upgrade tools and resources for your database environment that can help automate the process and make it easier for you. As part of these resources, there are several methods for upgrading or migrating the database to the new release that is supported, among which we can find:
- The database upgrade assistant, or DBUA for short, is a graphical user interface that walks you through the entire database upgrade process. You can launch DBUA via the Oracle Universal Installer or as a standalone tool anytime you need it.
- You can manually upgrade the database using the Parallel Upgrade Utility that enables you to perform the upgrade using shell scripts.
- You can migrate database data using the Oracle Data Pump resource that gives you export and import capabilities, performing a full or partial export from your database and then a full import exercise to the new database release.
- For a zero downtime option, you can use Oracle GoldenGate to synchronize the upgraded database.
- The Fleet Patching and Provisioning tool, previously known as Rapid Home Provisioning, help you complete a new database installation.
Of course, when thinking about upgrading your database, it’s crucial that you also consider the compatibility and interoperability between release numbers. Namely, you’ll be benefiting from new features that may be incompatible with your earlier release, which can lead to some unfortunate scenarios. So, how exactly does your database become incompatible with earlier releases?
- When a new feature stores data on disk that cannot be leveraged or processed by an earlier release
- When an existing feature does not behave as expected in the new environment
When addressing Oracle database compatibility, there’s one parameter in particular that helps you control the compatibility of your database, and that is the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter. It’s recommended that you increase the COMPATIBLE parameter after thoroughly testing an upgraded database; worth mentioning, once this parameter is to the max, you will not be able to downgrade the database.
In Database 19c, the COMPATIBLE parameter defaults to 19.0.0, allowing you to benefit from new Oracle Database 19c features as the upgraded database is now running in the required setting. The following table shows you how the COMPATIBLE parameter compares to releases proper to 19c.
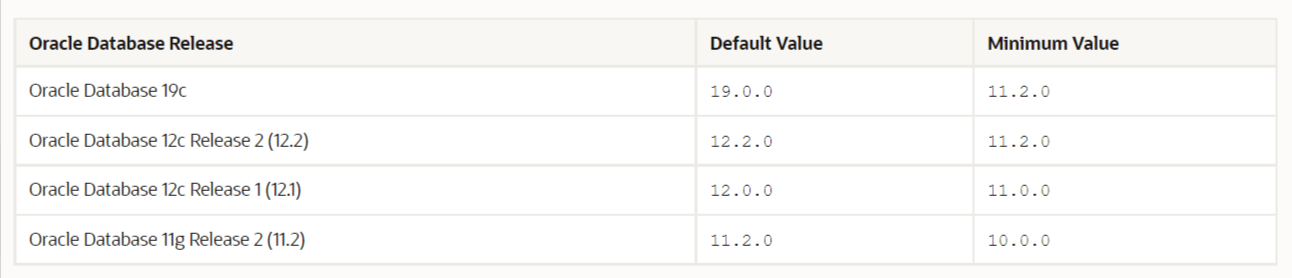
In the same context of upgrading your database, interoperability is about having different Oracle Databases communicate and work in a distributed environment. Interoperability is particularly important as the minimum requirements for a newer release may solicit that you upgrade the OS, which is why it’s essential that you must determine if all drivers, network, and storage are compatible when rolling out an upgrade.
Conclusion
To help you plan, we’ve prepared this ebook that lists out the features that are no longer supported in Oracle 19c so you can get a better understanding of the behavioral changes you will experience as you roll out the upgrade.

