Imagine a tool that has the potential to transform your workplace, making it more efficient and productive. That is where lies the true power of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and choosing the best RPA use cases is at the core of leveraging its functionality.
You might be wondering if RPA is the right fit for your business or specific functions within it. The good news is that RPA is incredibly versatile and excels at handling repetitive, rule-based tasks, and it doesn’t discriminate based on industry or function. If there’s at least one manual process in your organization that could benefit from increased efficiency, RPA is the answer.
But how can RPA unveil its multitude of benefits for your business? Well, this blog post dives into the ways how the best RPA use cases can streamline your business operations and boost productivity.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA describes the automated use of software “bots” to perform routine, rule-based tasks within business processes. Organizations can set up these software robots to mimic human behavior and interact with digital systems, applications, and data using RPA technology to complete activities like data entry, data extraction, form filling, and more.
It is commonly used in various industries, including finance, healthcare, customer service, human resources, and manufacturing, to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and free up human employees from mundane tasks so they can focus on more value-added activities. It is an important component of digital transformation strategies for many organizations.
| Need to scale up your automation game? No problem. RPA is infinitely scalable. |
| You can deploy a whole army of bots to tackle different processes, helping your organization become an automation powerhouse. |
- It decreases human errors, which are typically brought about by monotonous repetition of the same task.
- With RPA in place, employees are freed up to work on other duties that may ultimately prove to be more demanding when its applications handle the duplicate grunt work.
- It accomplishes jobs more quickly than humans, which results in quicker client response times. This is helpful when higher-ups on the corporate ladder demand quick turnaround on tasks.
- RPA tools can be used with legacy systems that are already in place without the requirement for complex software or extensive system integration. By using components like speech recognition and natural language processing, businesses may improve RPA even further. The robotic workforce may be modified to fit the peaks and troughs of the business’s workflow because robotic process automation is a very scalable asset.
Therefore, organizations who implement the best RPA use cases do so to raise productivity, add a degree of flexibility and agility, increase efficiency and speed, and reduce costs.
The Growing Importance of Robotic Process Automation in Modern Business
The robotic process automation market includes more than 60 vendors as of January 2023, but is becoming more consolidated and competitive. Banking and insurance followed by manufacturing have the highest demand representing a combined 40% of RPA vendors total customer count.
RPA can be used by businesses for a variety of tasks, including mass email creation, data extraction from media and scanned documents, invoice creation and sending, personnel history verification, and payroll automation. Since the goal of every organization is to make money, RPA can aid in quote-to-cash by automating sales procedures, which not only speeds up transaction execution but also improves accuracy. It can take over the full gamut of sales-oriented operational tasks, increasing customer satisfaction.
Robotic process automation excels in the area of data migration and management as well. Given the enormous amount of data available, having RPA to gather, integrate, analyze, and process the massive amounts of data produced in today’s commercial environment is a huge benefit.
It also enhances customer service operation and can be utilized to handle the simple, repetitive activities that burden customer service agents, freeing them up to provide better customer support.
Robotic process automation goes beyond merely automating discrete operations in sectors like banking and manufacturing where process complexity and regulations are paramount. Comprehensive end-to-end process automation is where RPA is headed in its evolution. Organizations who are starting this RPA journey frequently see the possibility to seamlessly incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) into their more general strategic goals.
Potential RPA Use cases
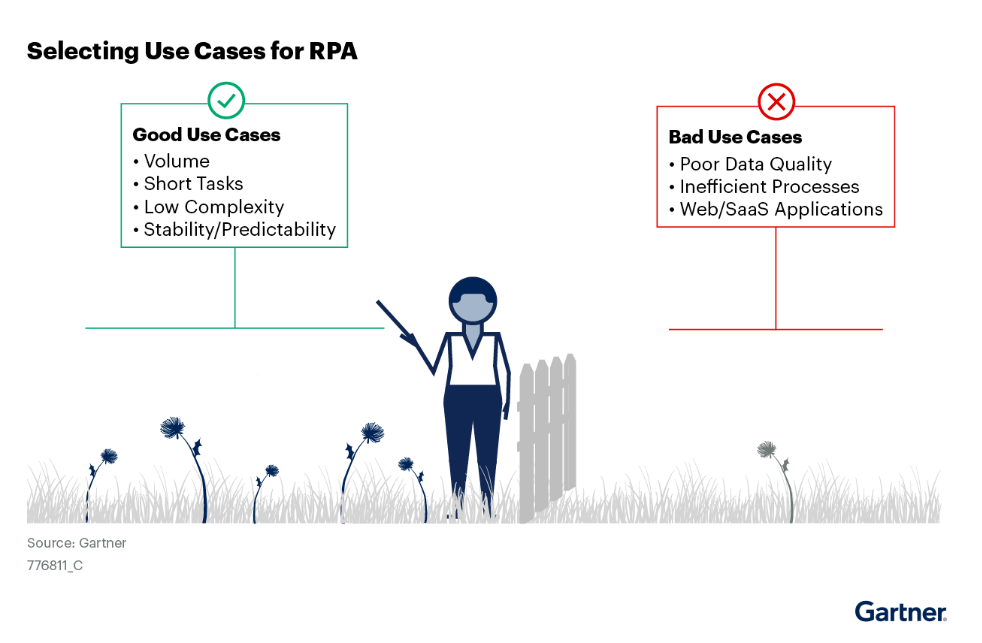
Nearly 50% of organizations using robotic process automation fail to achieve their process optimization goals. RPA initiatives fail because leaders select use cases that are complex, unstable or with too many dependencies.
So, What makes best RPA use cases
Since, robotic process automation automates the digital tasks that are repetitive, high-volume and rule-based, best RPA use cases are the ones that follow structure.
Criterion for Selecting the Best RPA Use Cases
| Key Consideration | Details |
| Significant Repetitive Tasks | Evaluate if the process occurs frequently enough to justify implementing robotic process automation. Calculate TCO per unit use case to ensure it’s lower than labor cost for a positive answer. Processes with irregular execution provide little ROI and are susceptible to unexpected changes. |
| Limited Scope | Assess the number of action items in a candidate process, which should not exceed 15. Focus on individual processes, not combinations, as robotic process automation is for task-level automation. Always optimize a task before automating for better ROI. |
| Lack of Complexity | Ensure use cases do not involve complex business rules, specifically no more than seven “if-else” blocks. These conditional statements must be in a manageable format. Simplify processes for improved ROI, as complex cases require more time for development and maintenance. |
| High Stability/Predictability | Examine the stability and susceptibility to change of the task to be automated. Review historical changes and planned modifications to assess stability. Robotic process automation for stable processes demands less maintenance and fewer updates. System stability is crucial for achieving better ROI. |
Bad RPA Use Cases
| Key Consideration | Details |
| Inefficient Processes | Automating inefficient processes can either hide their inefficiency or accelerate poorly designed processes. In such cases, RPA prolongs underlying issues and should not be applied without prior analysis. |
| Poor Data Quality | Robotic process automation systems typically transfer source data to other systems. If the source data is flawed, errors will propagate to downstream systems in the automation process, emphasizing the importance of data quality. |
| Integration with Changing Apps | SaaS and web applications that frequently change due to marketing updates or customer requirements may require frequent script updates. In such situations, API-first automation offers greater adaptability compared to RPA. |
Robotic Process Automation Services
From finance to healthcare, customer service to manufacturing, RPA is the secret weapon for streamlining operations, boosting efficiency, and liberating your human workforce from the monotony of repetitive tasks. It’s not just a technology; it’s a ticket to supercharging your organization’s productivity and embarking on a journey of digital transformation.




